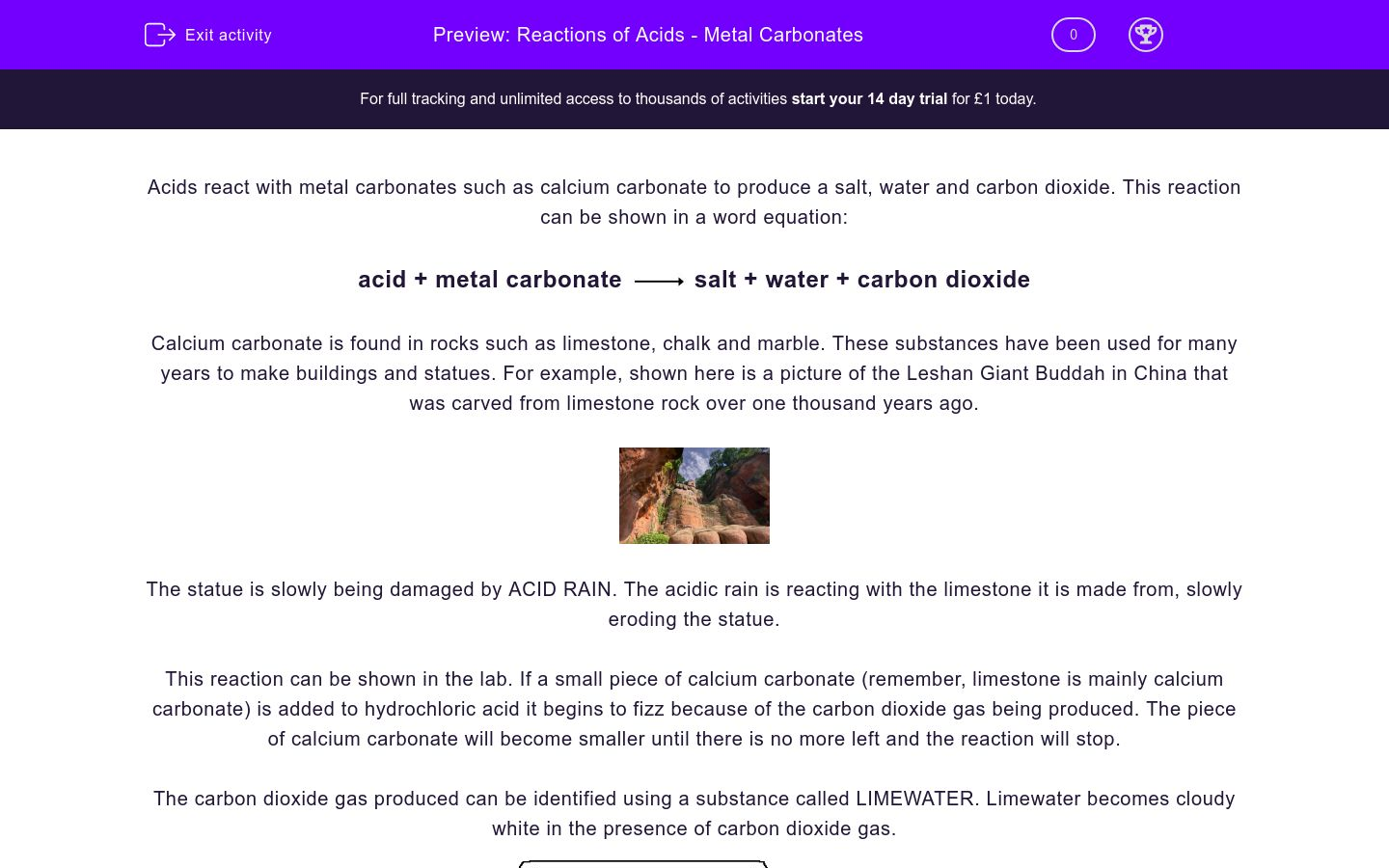
Marble Statues And Acid Rain Equation
Acid rain effects on buildings.
Marble statues and acid rain equation. Although many different types of stone have been used for sculpture the most vulnerable to potential acid rain damage are marble and limestone steiger 2015 the former is essentially a recrystallized form of the latter. Describe the chemical processes that cause limestone and marble statues to corrode. Acid precipitation affects stone primarily in two ways. Although these are recognized as highly durable materials buildings and outdoor monuments made of marble and limestone are now being gradually eroded away by acid rain.
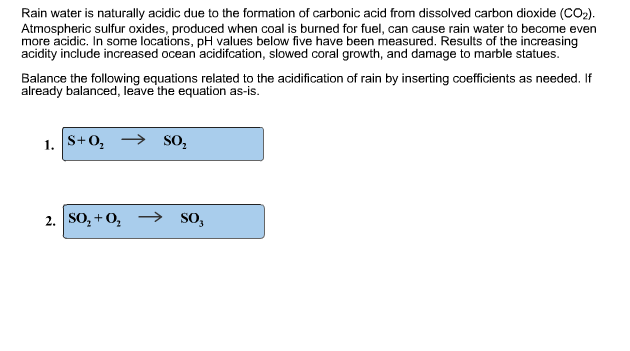
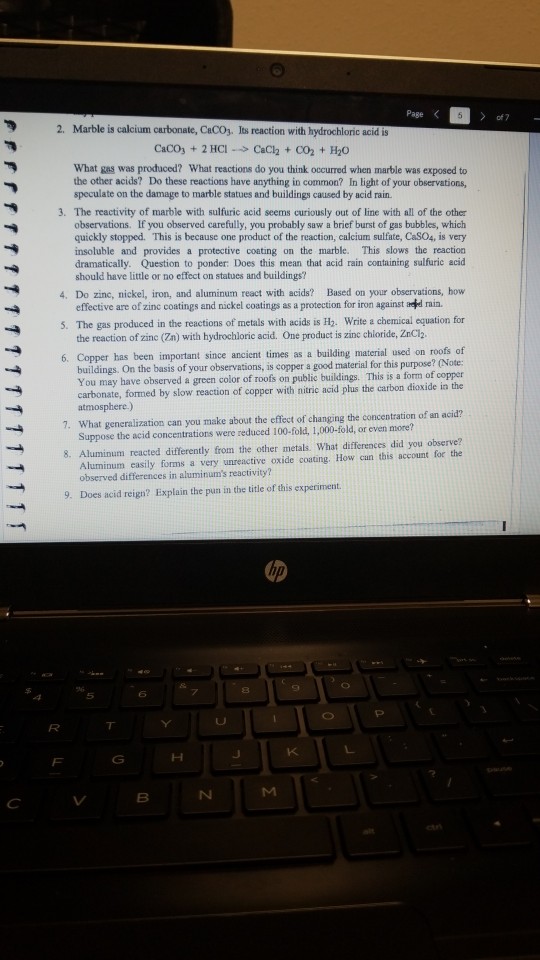
Metals like iron and calcium carbonate react with the acid in the rain slowly as follows. Acids have a corrosive effect on limestone or marble buildings or sculptures. How does acid precipitation affect marble and limestone buildings. Marble with its larger crystals and smaller pores can attain a high polish and is thus preferred for monuments and statues.
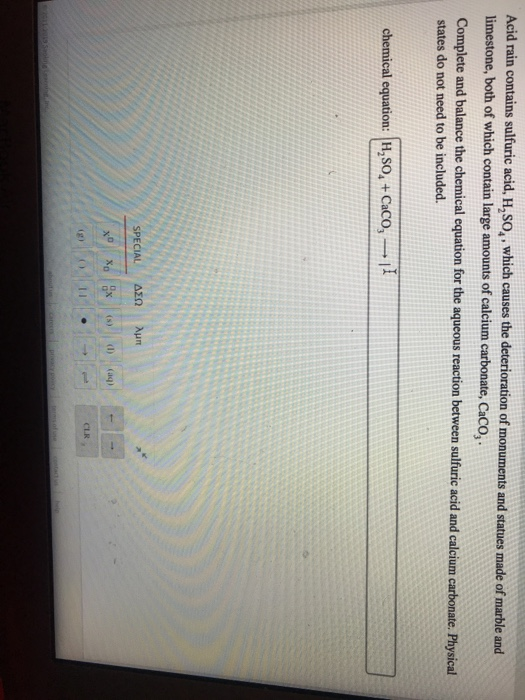
Sulfur dioxide plus water makes sulfurous acid. Caco 3 h 2 so 4 caso 4 h 2 o co 2. In exposed areas of buildings and statues we see roughened. Both marble and limestone consist of caco 3 which reacts with acid rain in an acid base reaction to produce caso 4.
Both are composed of calcite caco 3 other types of stone which are composed of silicate minerals such as granite or sandstone are intrinsically more resistant to acid attack. Caco3 s h2so4 aq caso4 aq co2 g h2o l caso4 is pretty insoluble stuff but it will dissolve in the large amount of water during the process of the degradation of the caco3 caused by acid rain. Figure 4 18 acid rain damage to a statue of george washington. How does acid rain ruin statues and monuments.
How does this happen. When sulfurous sulfuric and nitric acids in polluted air react with the calcite in marble and limestone the calcite dissolves. In exposed areas of buildings and statues we see roughened surfaces removal of material and loss of carved details. Balance the chemical equation for.
Effects of acid rain on the environment. It is well established that either wet or dry deposition of sulfur dioxide significantly increases the rate of corrosion on limestone sandstone and marble. Because caso 4 is somewhat soluble in water significant damage to the structure can result. Acid rain pollutes the air and corrodes buildings monuments and statues made of metals and marble.
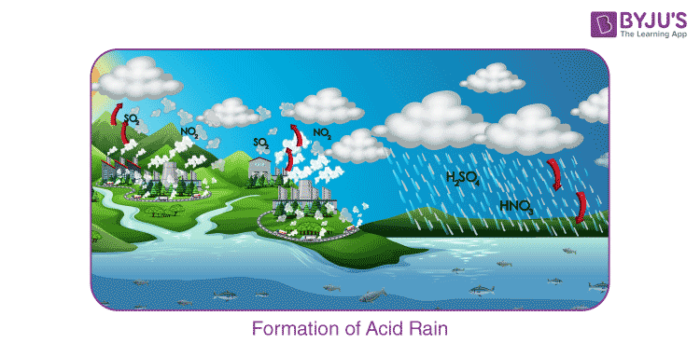
Acid rain contains carbonic nitric and sulfuric acid that are produced by oxidation and dissolution in water of gaseous oxides co 2 no 2 and so 2 present in the air as chemical pollutants. When sulfurous sulfuric and nitric acids in polluted air and rain react with the calcite in marble and limestone the calcite dissolves. Acid rains are one of the main degradation agents for marble artifacts. Marble like all calcareous rocks is particularly sensitive to degradation by acid chemicals and to weathering.